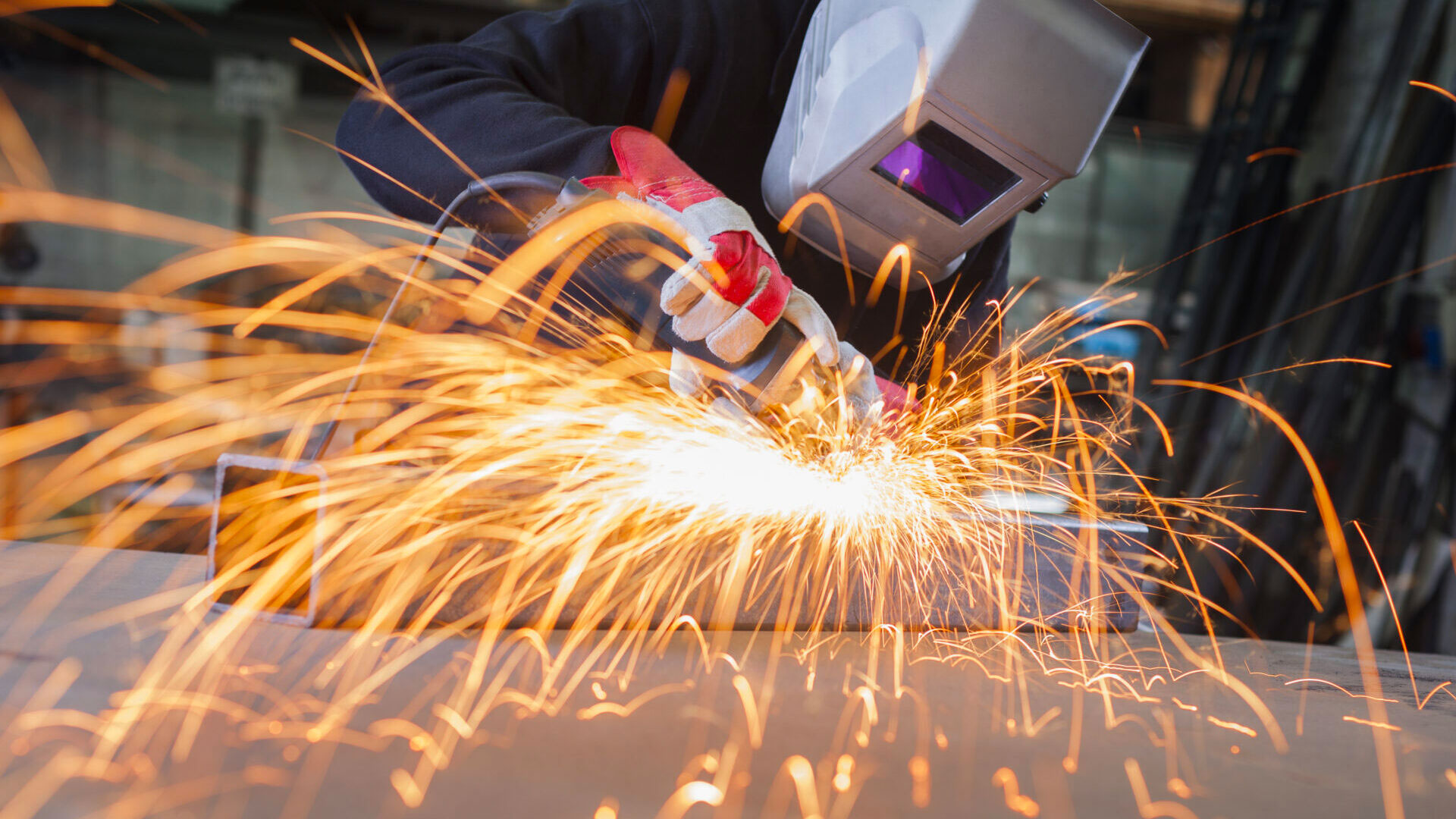
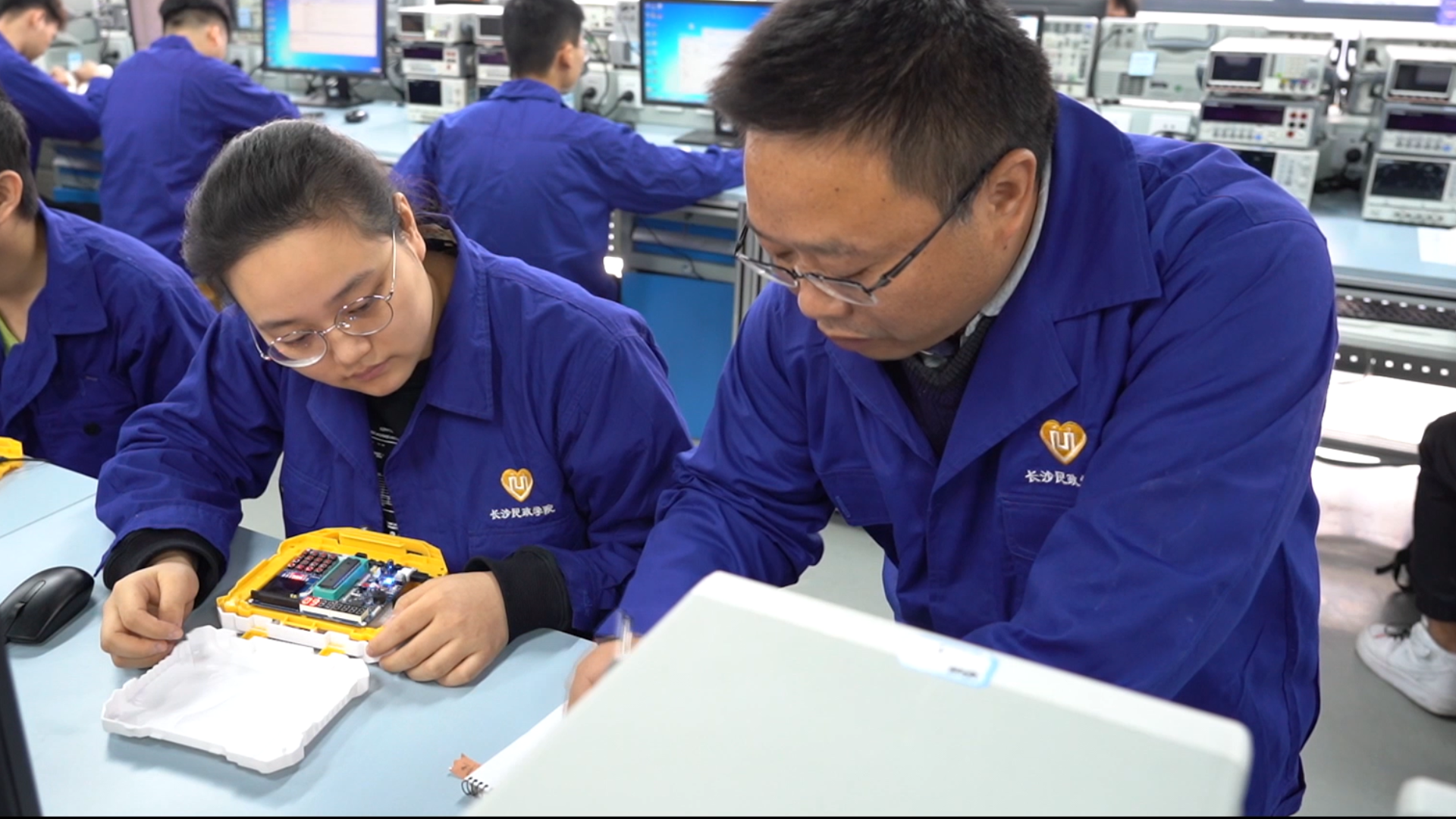
Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) is essential for economic development, supplying the skills required for the evolving labor markets. By aligning vocational education with industry needs, TVET enhances employability, reduces skills gaps, and boosts productivity. It plays a critical role in fostering inclusive growth, improving workforce quality, and ensuring a competitive edge in the global economy.
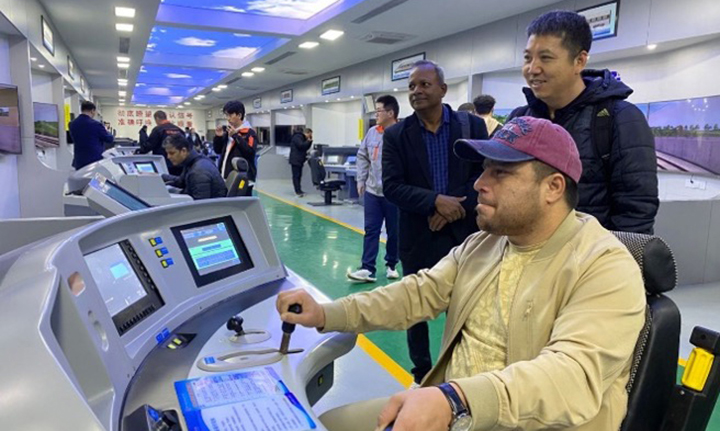
To support learning from a robust model of TVET development, ADB-PRC Regional Knowledge Sharing Initiative (RKSI) has financed a knowledge exchange for ten government officials and vocational school leaders from five Central Asian countries (Azerbaijan, Georgia, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan) to Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, located in southern People’s Republic of China (PRC) on 9–12 December 2024. The study tour was organized by Sectors Group Human and Social Development Sector Office (SG-HSD) and Central Asia Regional Economic Cooperation Program (CAREC) and also brought seven ADB sector specialists from Manila headquarters and several country offices. As a key gateway between PRC and Southeast Asia, Guangxi has been at the forefront of cross-border cooperation and benefitted from ADB-financed programs to enhance its TVET system. The knowledge exchange provided an opportunity to explore PRC’s best practices in modernizing its TVET system, focusing on industry partnerships, work-based learning, and income-generation activities, with insights from ADB-supported programs.
Policies and ADB’s Support on Guangxi’s TVET System
Guangxi has made significant policy efforts in advancing TVET, including the establishment of vocational education reform pilot zones in collaboration with the Ministry of Education in 2009–2013. In 2019, the region launched a program to build high-level vocational colleges, known as the “Double Excellence, Double High” initiative, which focuses on improving the quality of education and training. In 2023, Guangxi became a pilot province for the Ministry of Education’s modern vocational education system, solidifying its commitment to aligning TVET with industry needs.
A key driver of Guangxi’s progress was the Guangxi Modern TVET Development Program (2017–2022), co-financed by ADB and KfW Bankengruppe. This results-based lending program focused on improving the relevance, quality, and inclusiveness of TVET education. By aligning curricula with local labor market demands in the region’s priority growth sectors, the program helped equip students with practical skills, thereby improving employment opportunities, reducing the “skills gap” and driving regional economic development. The program received the 2021 ADB Best Performance Loan Project Award and benefited over one million students.
With the program now completed, its achievements have broader implications as a regional public good. Through facilitating cross-border knowledge exchange, particularly in areas like industry partnerships, curriculum development and the creation of international training bases, Guangxi has shared valuable lessons with neighboring countries.
Central Asia’s Challenges on TVET
Acute shortages of well-trained and job-ready workforce hinder Central Asian countries’ economic growth. Low quality of vocational skills, a mismatch between education and labor market needs, outdated infrastructure, and resource constraints limit the region’s ability to build a competitive workforce to align with the growing market demand. All Central Asian countries are taking measures to enhance their TVET systems, improve the quality and relevance of education, and develop better linkages with industry. Guangxi’s successful experiences, particularly in aligning TVET curricula with labor market demand and fostering cross-border cooperation, made it an ideal model to learn from.
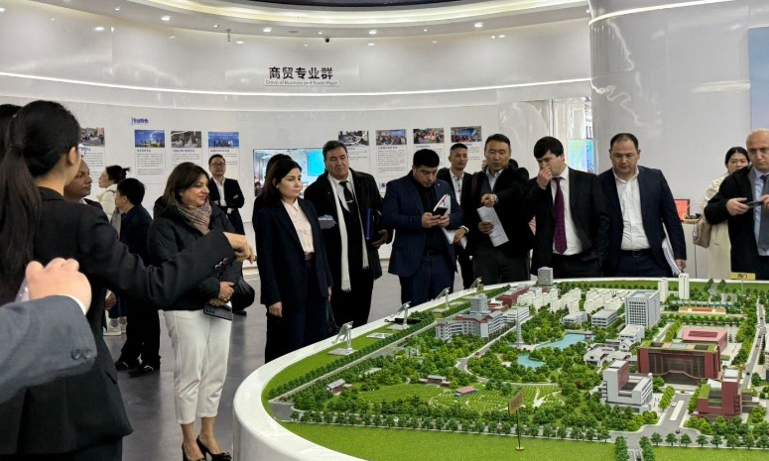

Guangxi’s Approach to TVET Development
Guangxi’s modernization of its TVET system stands out not only for its alignment with local industry needs but also for its emphasis on international cooperation—particularly with ASEAN countries. This strategic positioning, due to Guangxi’s proximity to Southeast Asia, has allowed the region to serve as a key platform for cross-border educational and technical exchanges, closely linked to supporting mutual economic benefits.
Among the key initiatives driving Guangxi’s success in TVET are:
- Strategic alignment: Guangxi’s TVET sector plans have been built on the central government’s Five-Year Plan(s), which ensured alignment of skills development with forecasted growth of priority sectors in the province – this was key in reducing the “skills mismatch” between TVET and labor market needs.
- Highly developed school-industry partnerships: Guangxi brought industry to the schools by setting up fully equipped operational workshops working under direct partnership arrangements with the industry and offering goods and services to the market. Colleges are incentivized by financial freedom and benefits that such partnership bring.
- Cross-border knowledge exchange and curriculum development: Guangxi has established platforms such as the China-ASEAN Vocational Education Exhibition and Forum, which facilitates the exchange of best practices in TVET. This forum has led to more than 100 signed projects, promoting curriculum development and industry training practices.
- Building overseas training bases: Guangxi has expanded its international reach by establishing China-ASEAN Modern Craftsmen Colleges. These institutions focus on building a highly skilled workforce, with a focus on the “Chinese + Vocational Education” model, enhancing both local and international faculty, and promoting cross-cultural exchanges in technical training.
- Preparing a tech-savvy workforce: With rapid technological advancements in recent decades and the growing need for a tech-savvy workforce to meet future demands, Guangxi has strategically aligned its TVET programs to cultivate a future-ready workforce across all sectors. Technologies such as big data, intelligent robotics, virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and other digital solutions are being seamlessly integrated into all vocational training areas. This tech-first approach, combined with the pervasive incorporation of technology throughout TVET, promises a bright future for workforce development.
- Internationalization of TVET: The China-ASEAN Vocational Education Cloud Platform allows the sharing of international teaching resources, benefiting vocational institutions across ASEAN countries. With over 199 shared resources, this platform enhances the quality of education across the region. Guangxi also offers scholarships to students from ASEAN countries, with over 1,000 students annually enrolled in vocational programs at Guangxi’s institutions. This exchange not only enhances the educational experience but also fosters long-term ties between China and its Southeast Asian neighbors.
Conclusion
Guangxi’s experience in modernizing its TVET system offers valuable lessons for Central Asia and beyond. The success of the ADB-supported Guangxi Modern TVET Development Program highlights the importance of aligning vocational education with industry needs, fostering international cooperation, and improving educational quality. As Central Asia faces similar challenges, Guangxi’s approach may serve as a model for enhancing TVET systems, promoting cross-border knowledge exchange, and developing skilled workforce.
Participants’ reflections:
“Azerbaijan can benefit from applying Guangxi’s best practices to improve vocational education by collaborating with both local industries and international partners, particularly in areas such as green energy and technological innovations. All these aspects provide valuable potential for adaptation and application in Azerbaijan, where reforms in vocational education and training are ongoing.”
Rustam Abdullaev, Head of the Vocational Education Policy Division, Ministry of Science and Education, Azerbaijan
“The knowledge gained about the Chinese TVET system significantly expanded our horizons. I was especially impressed by the acquaintance with the dual education system in colleges in Nanning and Guilin. We are grateful for the knowledge, which will certainly help us in further developing our systems.”
Myrad Kerjayev, Head of Ashgabat Secondary Professional School of Tourism, Turkmenistan